Glycemic Index Greek Yogurt is 93
Glycemic Index Greek Yogurt Nutritional Value
- Amount Per
- 100 grams
- Calories 59
- % Daily Value*
- Total Fat 0.4 g 0%
- Saturated fat 0.1 g 0%
- Polyunsaturated fat 0 g
- Monounsaturated fat 0.1 g
- Trans fat regulation 0 g
- Cholesterol 5 mg 1%
- Sodium 36 mg 1%
- Potassium 141 mg 4%
- Total Carbohydrate 3.6 g 1%
- Dietary fiber 0 g 0%
- Sugar 3.2 g
- Protein 10 g 20%
Description
Glycemic Index Greek Yogurt
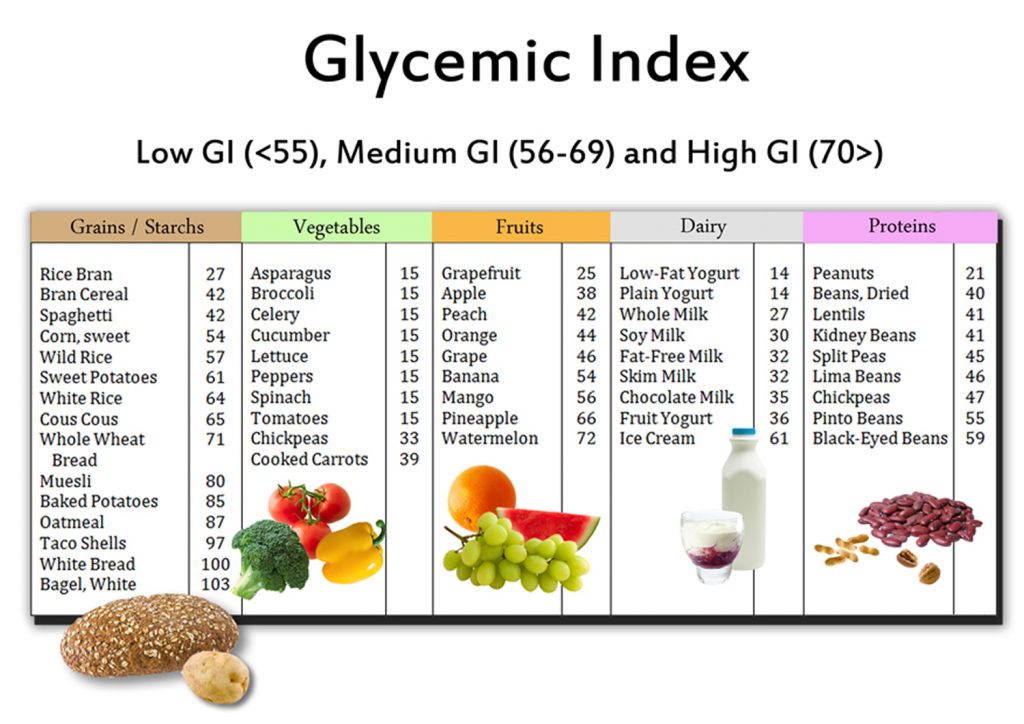
The Glycemic index is the number assigned to every food item. These numbers determine how many carbohydrates are present inside the food. A larger quantity of carbohydrates in food can impact our health negatively. Similarly, foods with low carbohydrates are easier to digest and healthier for our body.
Consumption of foods with low glycemic index value keeps the diabetic, and weight gain patient’s health maintained. Alternatively, high GI-value foods are less suitable for diabetic patients. Read more about Glycemic Index Greek Yogurt.
Glycemic Index Greek Yogurt:
Yogurt is one of the most popular foods that is preferably consumed in breakfast. With the juicy and creamy taste and the numerous nutrients, yogurt serves as everyone’s favorite food. Other than breakfast, people also consume it in other meals. Yogurt is a part of many dishes, being an essential part.
There are different yogurt types, including Greek yogurt, plain yogurt, Australian yogurt, and Icelandic. These common types of yogurt are popular yogurt in different regions. Among all, Greek Yogurt is the most creamy and thick. This nutrient-dense food is highly suitable for consumption in all health conditions. The sweetened Greek yogurt is low on carbohydrates. This Greek yogurt also has more proteins inside. Together, these two properties ensure that Greek yogurt consumption doesn’t cause a blood sugar spike. So the glycemic index of Greek Yogurt is lesser than other food types.
Along with Greek yogurt, plain yogurt also has less GI-value. But the GI-value depends more on how you eat your yogurt. If you combine high-GI foods with Greek yogurt, it can be a balanced or high-GI diet.
In the end, the unsweetened glycemic index of Greek yogurt is very low. But sweetened Greek yogurt has more fats. So if you have fat issues, you should consume unsweetened Greek yogurt. In both ways, Greek yogurt is suitable for all health conditions with its low GI value.
About Greek Yogurt
In the relatively recent past, Greek yogurt was viewed as an intriguing alternative. Today, it’s as omnipresent as ordinary dairy yogurt. Most buyers offer a major go-ahead as its would prefer – tangier, less sweet and creamier than traditional “ordinary” yogurt produced using entire milk. However, is Greek yogurt more advantageous than its ordinary partner? Also, shouldn’t something be said about the wide exhibit of different sorts of yogurts?
To begin with, honestly: Greek and customary yogurt, in their plain, nonfat or low-fat structures, just as the wide assortment of plant-based and premium yogurts, can be essential for an empowering diet. They’re low in calories and pressed with calcium and live bacterial societies.
In any case, our Mediterranean companion – which is stressed widely to eliminate a significant part of the fluid whey, lactose and sugar, giving it its thick consistency – has an unquestionable edge. In generally similar measure of calories, it can get together to twofold the protein, while cutting sugar content significantly.
Those are “two things dietitians love,” says Dawn Jackson Blatner, an enlisted dietitian and creator of “The Flexitarian Diet.” “For somebody who needs the creamier surface, a tad of a protein edge and a sugar decline, going Greek is unquestionably not all publicity.” So this concludes the topic for Glycemic Index Greek Yogurt